https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/economy/india-s-unemployment-rate-doubled-in-two-years-soe-in-figures-64953
While unemployment remains high in both urban and rural India, job hunting is a bigger challenge for the young and the educated, notes CSE’s State of the Environment in Figures
By Kiran Pandey
Last Updated: Thursday 06 June 2019

India’s rate of unemployment doubled in the past two years, according to the State of India’s Environment (SoE) In Figures, 2019. This has particularly affected young graduates.
According to the report, the unemployment rate has gone up from four per cent to 7.6 in the last two years (May 2017-April 2019). The unemployment rate in April 2019 was the highest in two years. The rate for rural areas in this month was also the highest in this period.
SoE in figures was released by Delhi-based non-profit Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) on World Environment Day. The data for it has been provided by the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), New Delhi.

Young Indians (aged 15-24 years) constitute nearly a fifth of India’s total population, according to the country’s 2011 Census. By 2020, they are predicted to make up a third of the country’s population.
The report notes that the youth (between 20-24 years), who constitute around 40 per cent of India’s labour force, have an unemployment rate of 32 per cent.
The unemployment rate among the educated is even worse. The rate among people with at least a graduate degree was 13.17 per cent in September-December 2018, up from 10.39 per cent in May-August 2017.
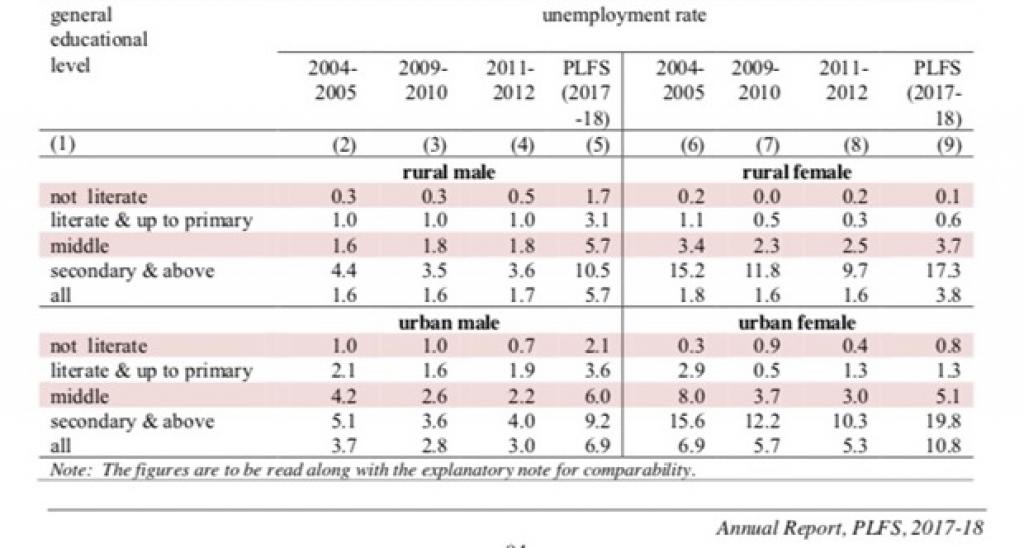
 The Periodic Labour Force Survey for 2017-18 released by National Sample Survey Office too shows that unemployment rate increased with education level.
The Periodic Labour Force Survey for 2017-18 released by National Sample Survey Office too shows that unemployment rate increased with education level.
According to SoE in Figures, 2017, a major cause for high unemployment rates in India is the lack of skills required for jobs that are available. This is worrying because India is a young country — home to 20 per cent of the world’s young population — and a major portion of this young workforce, though educated, is unskilled.
Official figures validate this. The Union Ministry Of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship says 4.69 per cent of India’s total workforce is formally skilled, as against 52 per cent in the United States, 68 per cent in the United Kingdom, 75 per cent in Germany, 80 per cent in Japan and 96 per cent in South Korea.
So why do young, educated Indians have poor job skills? One reason is that India has a limited number of quality institutes in spite of growth in the number of higher education providers.
A ray of hope
The World Bank recently estimated that India needs to create 8.1 million jobs a year to maintain its employment rate, which has been declining.
Given India’s demographic dividend and urgency to create jobs, the manufacturing sector could prove to be a large employer that provides decent income opportunities.
For example, rapid modernisation of the food processing sector could be one way of increasing its export potential as well as improving employment elasticity-to-growth and investment in it.
With a rise in per capita income, domestic demand for processed food would also rise, making the sector a viable option for pushing manufacturing growth and employment.
Removing structural bottlenecks to the manufacturing sector is key to promoting job creation in more productive and better-paid activities, according to an OECD report on economic outlook released in May 2019.
The International Labour Organization predicts India will have 18.9 million jobless people in 2019. Even as India’s economy is projected to grow 7.5 per cent by 2020, will this growth translate into jobs?
Santosh Kumar Gangwar, who took charge as the Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Labour and Employment in the newly elected government, has a tough job ahead.
According to the report, the unemployment rate has gone up from four per cent to 7.6 in the last two years (May 2017-April 2019). The unemployment rate in April 2019 was the highest in two years. The rate for rural areas in this month was also the highest in this period.
SoE in figures was released by Delhi-based non-profit Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) on World Environment Day. The data for it has been provided by the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), New Delhi.

Young Indians (aged 15-24 years) constitute nearly a fifth of India’s total population, according to the country’s 2011 Census. By 2020, they are predicted to make up a third of the country’s population.
The report notes that the youth (between 20-24 years), who constitute around 40 per cent of India’s labour force, have an unemployment rate of 32 per cent.
The unemployment rate among the educated is even worse. The rate among people with at least a graduate degree was 13.17 per cent in September-December 2018, up from 10.39 per cent in May-August 2017.
 The Periodic Labour Force Survey for 2017-18 released by National Sample Survey Office too shows that unemployment rate increased with education level.
The Periodic Labour Force Survey for 2017-18 released by National Sample Survey Office too shows that unemployment rate increased with education level.According to SoE in Figures, 2017, a major cause for high unemployment rates in India is the lack of skills required for jobs that are available. This is worrying because India is a young country — home to 20 per cent of the world’s young population — and a major portion of this young workforce, though educated, is unskilled.
Official figures validate this. The Union Ministry Of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship says 4.69 per cent of India’s total workforce is formally skilled, as against 52 per cent in the United States, 68 per cent in the United Kingdom, 75 per cent in Germany, 80 per cent in Japan and 96 per cent in South Korea.
So why do young, educated Indians have poor job skills? One reason is that India has a limited number of quality institutes in spite of growth in the number of higher education providers.
A ray of hope
The World Bank recently estimated that India needs to create 8.1 million jobs a year to maintain its employment rate, which has been declining.
Given India’s demographic dividend and urgency to create jobs, the manufacturing sector could prove to be a large employer that provides decent income opportunities.
For example, rapid modernisation of the food processing sector could be one way of increasing its export potential as well as improving employment elasticity-to-growth and investment in it.
With a rise in per capita income, domestic demand for processed food would also rise, making the sector a viable option for pushing manufacturing growth and employment.
Removing structural bottlenecks to the manufacturing sector is key to promoting job creation in more productive and better-paid activities, according to an OECD report on economic outlook released in May 2019.
The International Labour Organization predicts India will have 18.9 million jobless people in 2019. Even as India’s economy is projected to grow 7.5 per cent by 2020, will this growth translate into jobs?
Santosh Kumar Gangwar, who took charge as the Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Labour and Employment in the newly elected government, has a tough job ahead.